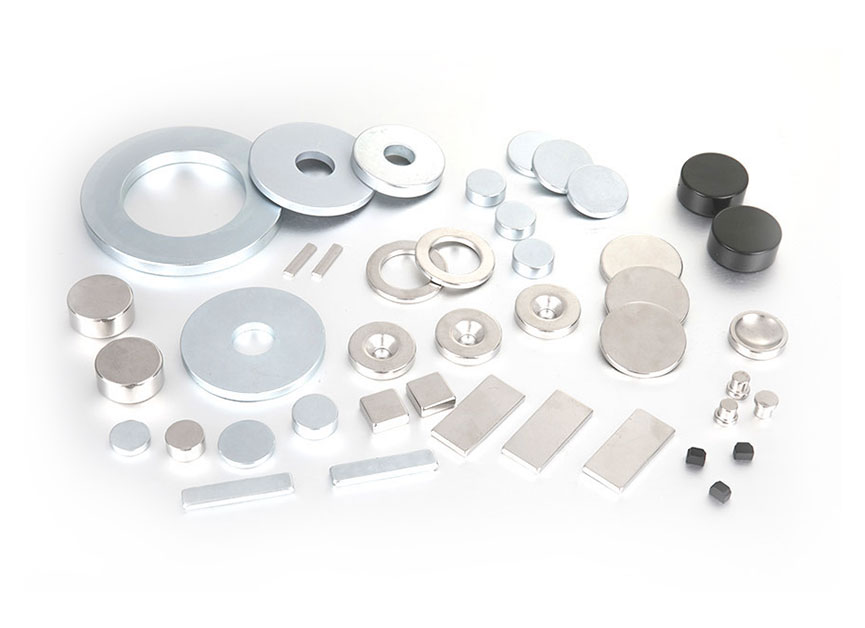
Sintered NdFeB permanent magnet materials are divided into low coercive force (N), medium coercive force M, high coercive force H, super high coercive force SH, ultra-high coercive force UH according to the coercive force of magnetic polarization strength , High coercivity EH category six products.
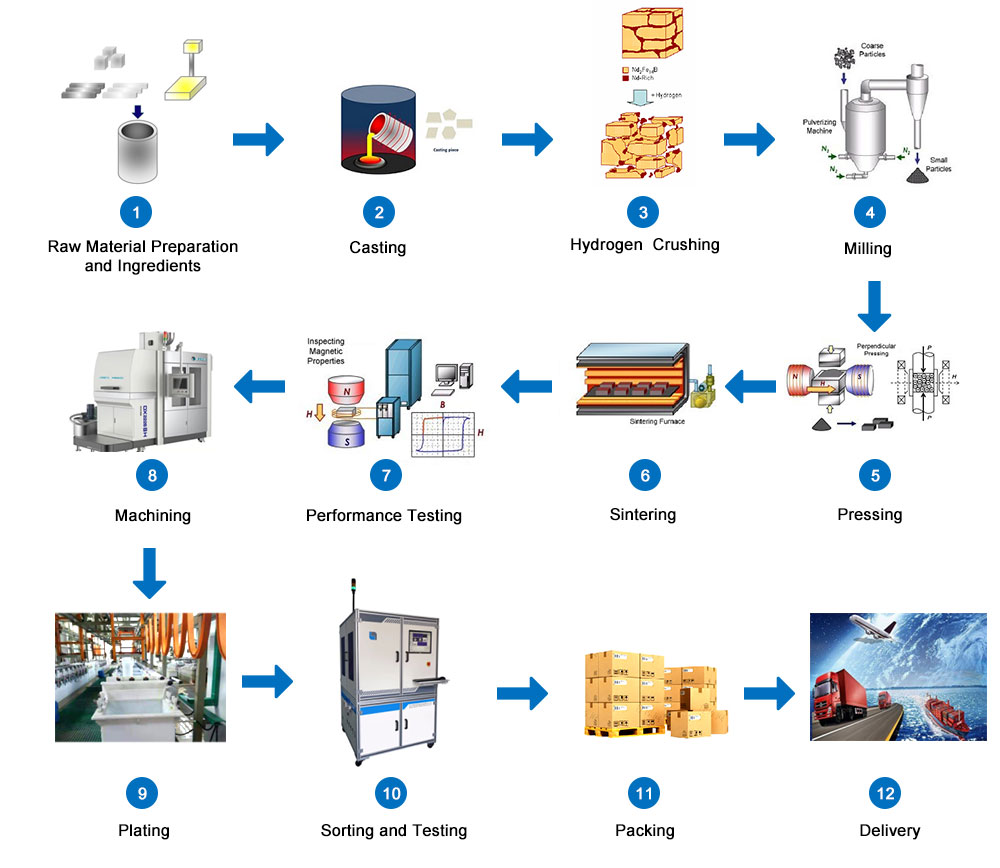
1. Composition design: The composition design of sintered NdFeB is very important. It relates to whether the product quality and magnetic performance indicators can meet customer requirements, because many intrinsic magnetic properties of the material, such as magnetic polarization, Curie temperature, etc. It is determined by the composition of the material. The basic principle of composition design is to ensure a sufficiently high intrinsic performance, while comprehensively considering material costs. (The cost of raw materials accounts for about 65%-90% of the total cost of sintered NdFeB materials. Under the premise of meeting the user's magnetic performance requirements, cheap components should be used as much as possible, and rare earth metals and other precious metal materials should be used less)
2. Smelting ingots/slices: Smelting is the first process for sintered NdFeB magnets to enter the production process. The smelting furnace produces alloy strips. The process requires furnace temperature to reach about 1300 degrees and lasts for four hours to complete . After this process, the raw materials are processed into alloy flakes by heat melting and cooling, and then proceed to the next process.
3. Powdering: The purpose of powdering is to crush large alloy ingots into powders of a certain size. The commonly used powdering process is to make NdFeB spin strips (SC tablets) through hydrogen crushing and jet milling. In order to obtain a well-oriented magnet, the powder particles are required to have a small size (3-4μm) and a concentrated size distribution, and the powder particles are spherical or nearly spherical.
4. Orientation and compaction: In the last issue, I have introduced the magnetic orientation of sintered NdFeB. Powder magnetic field orientation is one of the key technologies for producing high-performance sintered NdFeB. After the crushed magnetic powder is loaded into the mold, an external magnetic field is applied for orientation, and the powder is compacted after orientation. At present, there are three types of molding methods commonly used: membrane pressure, mold pressing and cold isostatic pressing and rubber mold isostatic pressing. With the same neodymium content, rubber mold isostatic pressing can obtain a larger magnetic energy product.
5. Sintering and tempering: The relative density of the sintered NdFeB powder compact is relatively large, the contact between the particles is mechanical contact, and the bonding strength is low. In order to further increase the density, improve the contact properties between the powder particles, and increase the strength, To make the magnet have the microscopic characteristics of high permanent magnetic performance, it is necessary to heat the compact to a temperature below the melting point of the basic phase of the powder, and heat treatment for a period of time. This process is called sintering.
After the sintered magnet is quenched at a high temperature, the grain boundary phase distribution is uneven and the grain boundary is not clear. Therefore, it is necessary to temper at a certain temperature to optimize the structure to obtain better magnetic properties. Tempering refers to cooling the sintered magnetic powder blank to a certain temperature and then heating it up again. The tempering temperature needs to be determined by experiment or thermal differential analysis.
6. Machining and surface treatment: There are various shapes of sintered NdFeB magnets that are actually used, such as discs, cylinders, rings, squares, tiles, sectors and various irregular shapes. Due to the different shapes and sizes of permanent magnet elements, in the production process, except for large-sized regular permanent magnet elements, other magnets are difficult to be molded at one time. Therefore, generally in the powder metallurgy process, Mr. produces large pieces of blanks, after sintering and tempering, and then through mechanical processing (including cutting, punching, etc.), grinding processing, and surface coating processing to produce products that meet customer needs Magnetic materials of shape and size. There are 3 types of machining, including
1. Cutting cylindrical and square columnar magnets into disc-shaped and square-shaped elements is called cutting
2. Machining round and square magnets into fan-shaped, tile-shaped, or grooved or other complex-shaped magnets is called contour processing
3. Machining round bar and square bar magnets into cylindrical or square cylindrical elements is called drilling
The machining methods include grinding and slicing, electric discharge cutting and laser processing.
7. Quality inspection: The quality inspection and product quality inspection during the production process of sintered NdFeB permanent magnets should include the items listed in the following table, but not every item must be inspected, which needs to be determined by the requirements of the product order contract. Decided.


 sales00@jlmagnet.com
sales00@jlmagnet.com