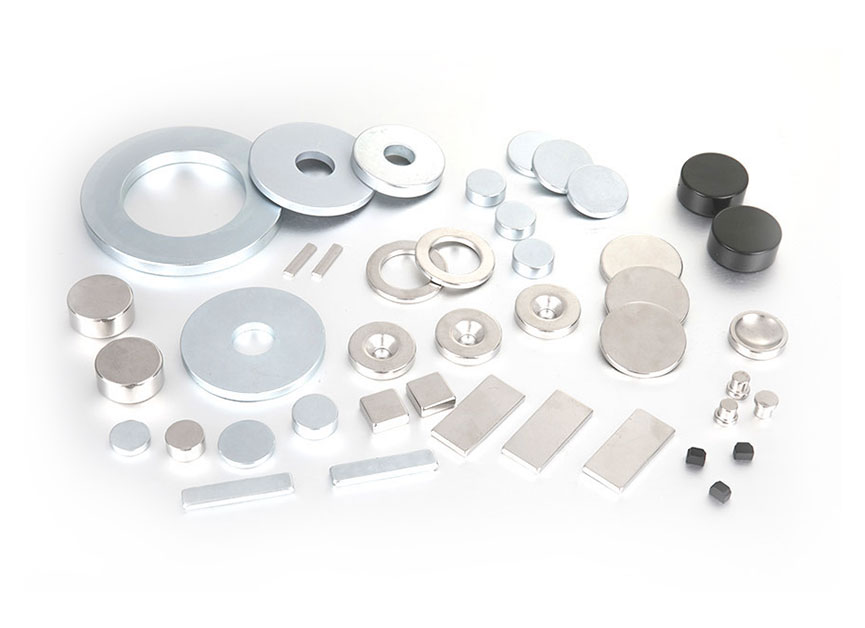
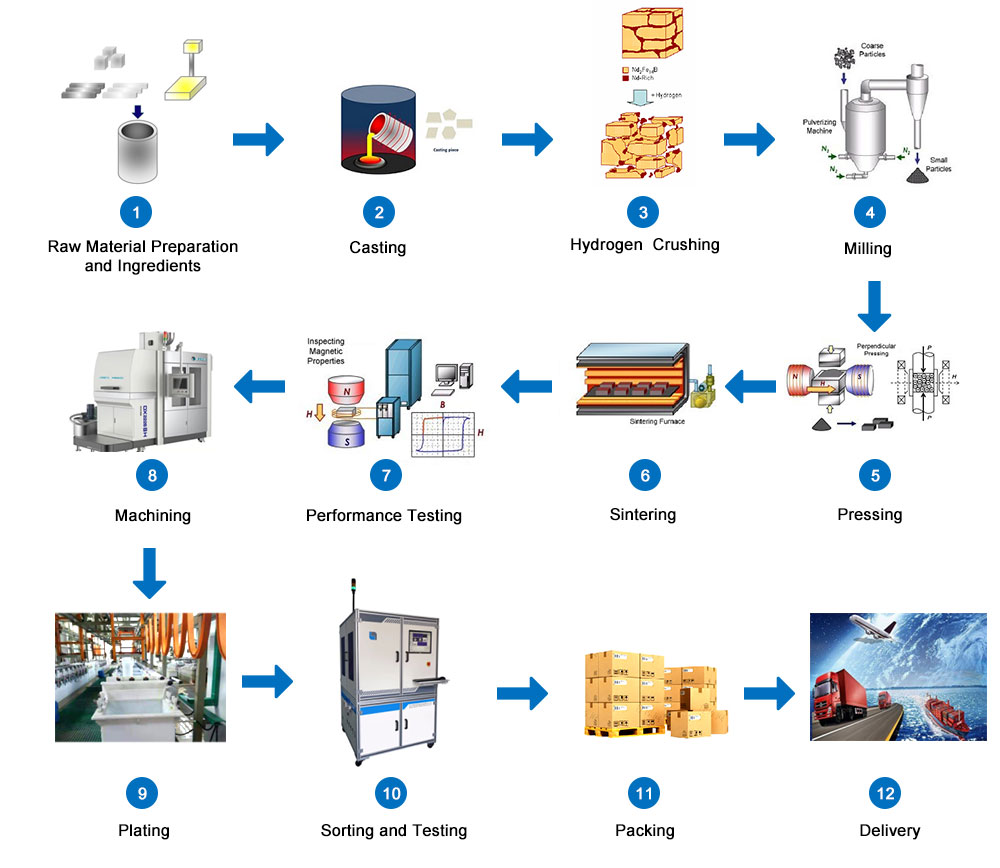
Nd Febs are low density, high-precision alloyed graphite materials with high electrical and magnetic properties. These are highly useful in applications requiring strong attachment to non-magnetic surfaces. In this way, using the raw material, shapes can be produced through casting or pressing.
NDFeb is one of the most widely used materials in the production of high quality electromagnets. The material has a number of advantages over other common raw materials for the purpose of electrochemical applications. Besides, it has a long history of successful fabrication and use. NDFeb is prepared through a series of processes starting from preparative stage to dielectric heating. It is characterized by high-precision dielectric heating-turbulent dielectric melting processes, which result in the production of a variety of different types of magnets produced through various processes:
This is accomplished through the coiling of magnetized powder. The sintered nDFeb powder is supplied in a package of individual pellets, each of which is coated with different sized magnetized particles. These pellets are then pressed into an aluminum or steel tray, where they undergo a series of temperature and pressure treatments, which bring about the generation of different varieties of high quality permanent magnet materials. While each type of magnet is characterized by different thicknesses, surface textures, and other physical characteristics, all of them are made from the same raw materials and have the same expected performance, which is a drastic reduction in manufacturing costs. Moreover, due to their uniformity in size and shapes, these sintered NDFeb magnets can be used interchangeably for a variety of electrochemical applications.
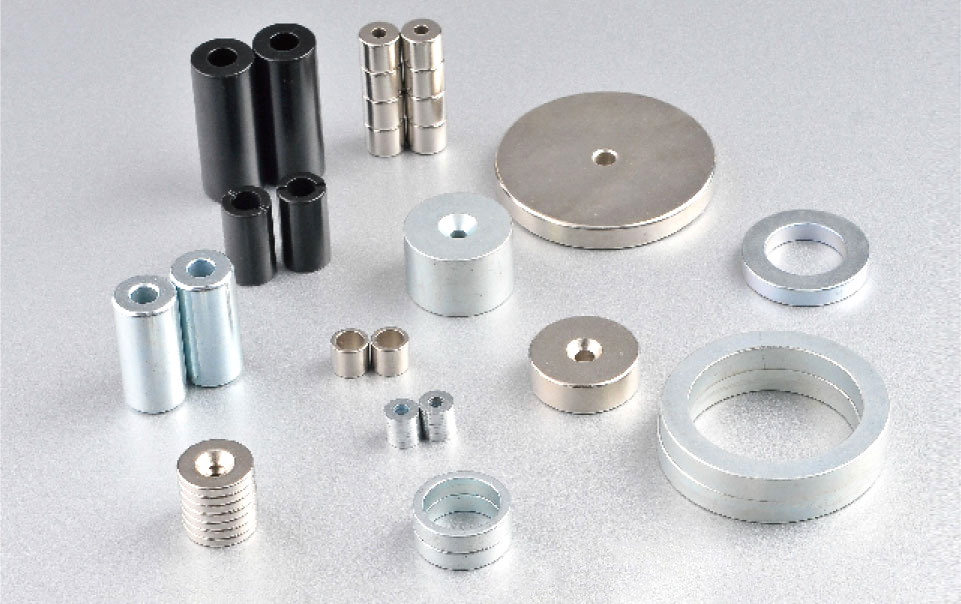

In addition, using this NDFeb powder as a building block, various ceramic materials can be made. The ceramic magnets that result from the coiling of the powder particles magnetic field are then shaped into any shape imaginable, which includes being flat, cylindrical, and even oblong. The unique property of this particular magnet powder makes it ideal for use in designing different kinds of ceramic materials.
Another way to utilize this product is by the development of a dielectric device, such as those seen in the Sintered NdFeB Magnet. The coiling of the powder generates a favorable internal magnetic field, which is observed by means of a small magnet attached to the inside of a sample plate. This method is often referred to as the "sag" method, because the metal attachment at the center of the sample plate is referred to as a sag. Consequently, a metal attachment at the bottom portion of the plate is termed a "grain boundary," whereas a metal attachment at the top portion is called a "grain."
Sintered NdFeB Magnet particles are shaped as spherical grains when they are placed in a magnetic field, which causes them to grow into an array that is referred to as a "grain boundary." These grain boundaries help the magnets to develop the ideal level of corrosion resistance for these types of alloys. Because these alloys contain non-ferrous metals such as nickel and chromium, manufacturers have designed special products that will allow these materials to be incorporated into their products without significant risk of the components falling apart due to corrosion.


 sales00@jlmagnet.com
sales00@jlmagnet.com