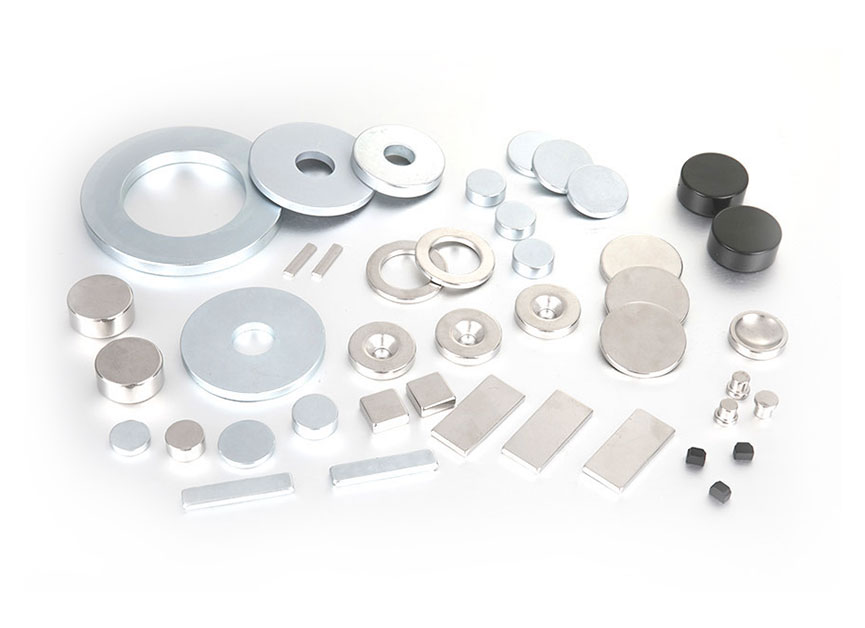
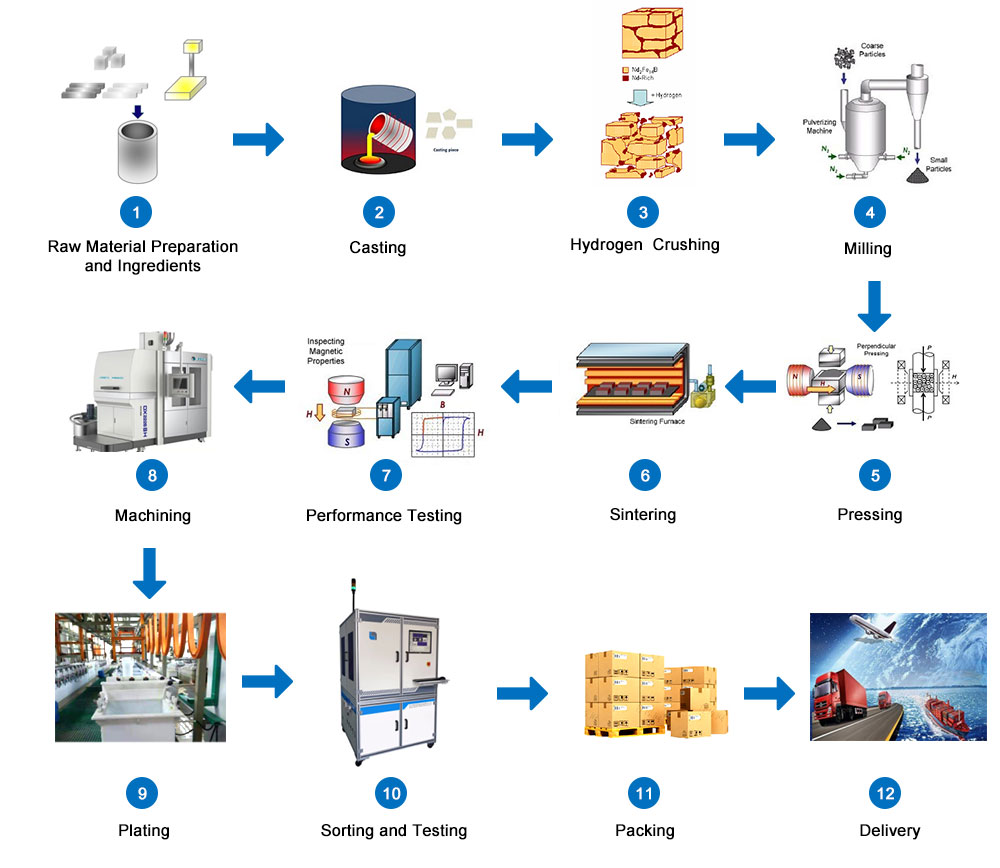
NdFeB process flow
1. Raw material preparation and pretreatment
Process introduction: pretreatment of raw materials such as weighing, crushing, material breaking and rust removal.
Process equipment: steel bar cutting machine, drum polishing machine, etc.
2. Smelting
Process introduction: The pretreated raw materials, such as neodymium, pure iron, and iron boron, are added in a vacuum melting furnace according to the proportions, and they are smelted at high temperature under the protection of argon, and then stripped. Make the product composition uniform, high crystal orientation, good organization consistency, and avoid the generation of ɑ-Fe.
Process equipment: vacuum melting furnace
3. Hydrogen explosion
Process introduction: The hydrogen explosion (HD) process uses the hydrogen absorption properties of rare earth intermetallic compounds to place the neodymium-iron-boron alloy in a hydrogen environment. The hydrogen enters the alloy along a thin layer of neodymium-rich phase, causing it to expand, burst and break. The cracks in the neodymium-rich phase layer ensure the integrity of the main phase grains and the interphase of the neodymium-rich grain boundaries. The HD process makes the NdFeB spinner very loose, which greatly improves the powder making efficiency of the jet mill and reduces the production cost.
Process equipment: vacuum hydrogen treatment furnace
4. Flour milling
Process introduction: The jet mill powder is crushed by the high-speed collision of the material itself, which has no abrasion and pollution to the inner wall of the mill, and can produce powder at a high rate.
Process equipment: jet mill
5. Molding orientation
Process introduction: The function of orientation is to turn the easy magnetization direction c axis of chaotically oriented powder particles to the same direction, so as to obtain large remanence. The main purpose of compaction is to crush the powder into a certain shape and size, while maintaining as much as possible the crystal grain orientation obtained in the magnetic field orientation. We design to use a forming magnetic field press and an isostatic press for secondary molding. For special-shaped magnets, special mold tooling is used for direct molding. The sintered magnets can be put into use after a little surface treatment, which greatly saves materials. And subsequent processing costs.
Process equipment: magnetic field press, isostatic press
6. Sintering
Process introduction: Sintering is a series of physical and chemical changes that cause crushing at high temperatures. It is a simple and inexpensive way to change the microstructure of the material to improve the magnetic properties of the material. Sintering is the post-forming process of the material, which has an extremely important influence on the density and microstructure of the magnet.
Process equipment: vacuum sintering furnace
7. Machining
Process introduction: The neodymium iron boron magnets obtained after sintering are all blanks, which require further machining to obtain products of various sizes, sizes and shapes. Due to its brittleness and poor mechanical properties, NdFeB magnets can only be processed by grinding and cutting.
Process equipment: surface grinder, double end grinder, chamfering machine
8. Surface treatment
Process introduction: Surface treatment of rare earth permanent magnets of various shapes, such as electrophoresis, zinc plating, nickel, nickel copper nickel and phosphating, etc., to ensure the appearance and corrosion resistance of the product.
9. Finished product inspection and packaging
Process introduction: The products are tested for various magnetic properties, corrosion resistance, high temperature performance, etc., and packaged after reaching the standard to meet the various needs of customers.
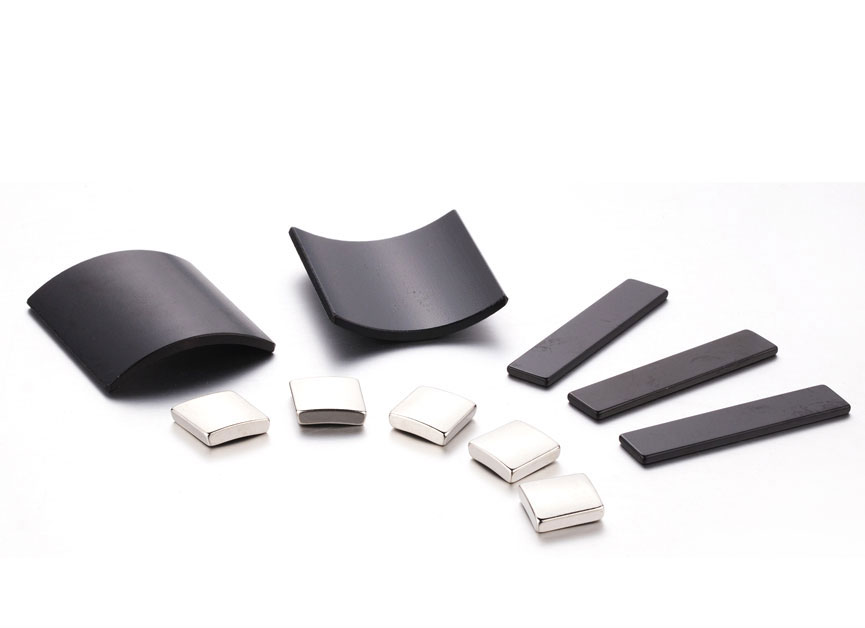

The main component of the magnet is Nd2Fe14B, which has extremely high magnetic properties. Its maximum magnetic energy product (BH) max is more than 10 times higher than that of ferrite. The maximum working temperature can reach 250℃. The mechanical properties are also quite good, which can be suitable for grinding. Different processing methods such as wire cutting and drilling; due to poor corrosion resistance, different coating treatments must be applied to the surface according to different requirements


 sales00@jlmagnet.com
sales00@jlmagnet.com