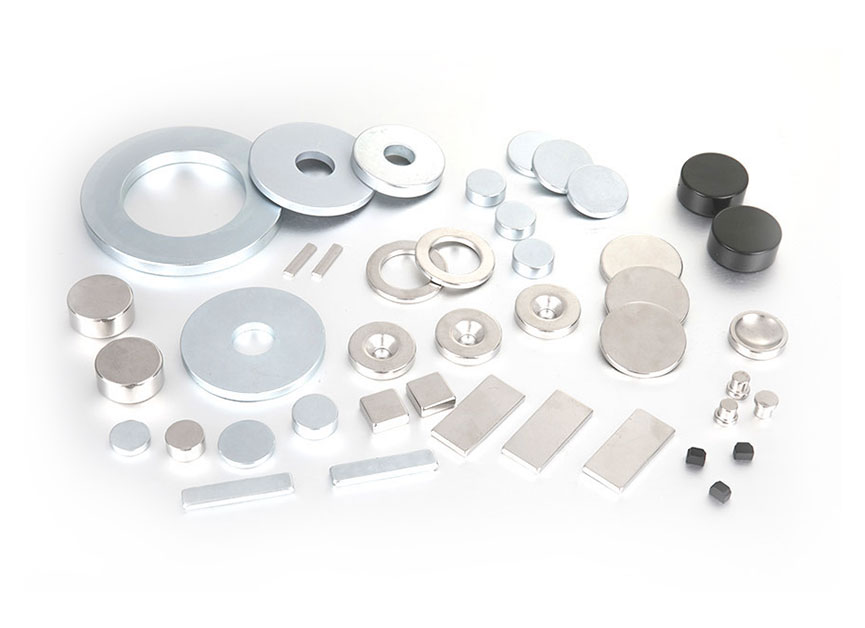
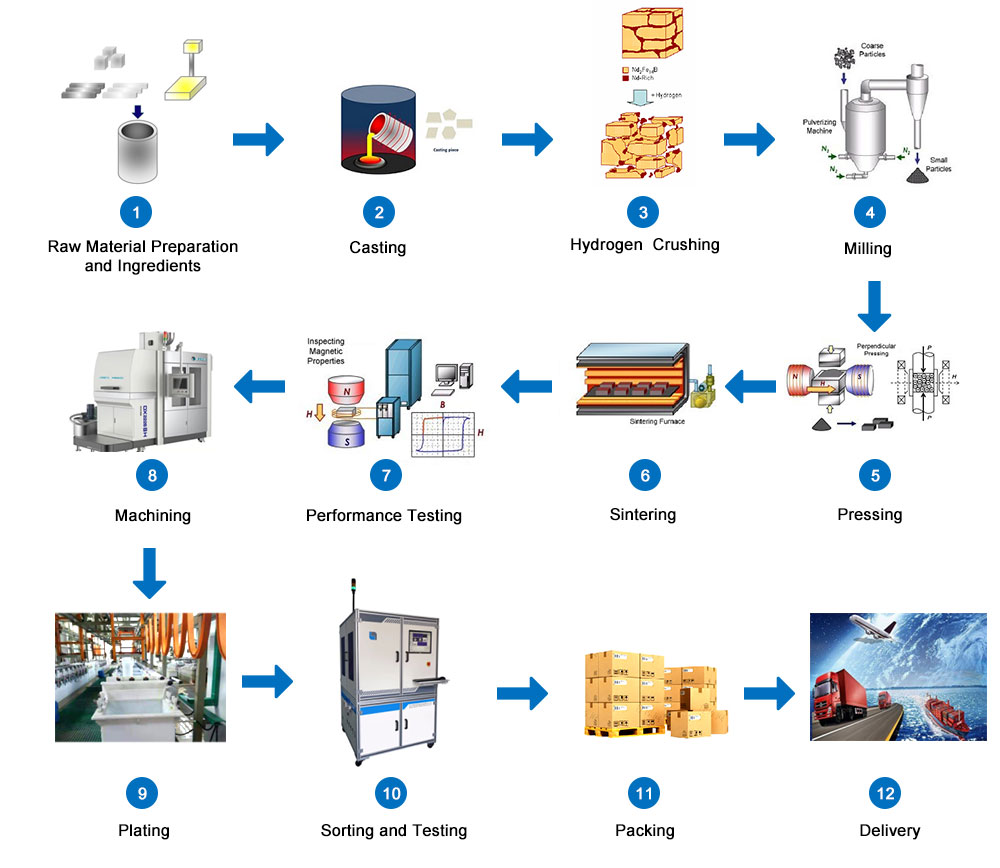
A motor magnet is used to power an electric motor. These motors are different from the usual type of electric motors in that they use permanent magnets in addition to windings on the field. Using a magnet is a more efficient way to drive a motor. If you're looking for more information on this type of electric dynamo, read on. This article will provide you with more information on the benefits of a permanent-magnet motor and how you can install one for your home or business.
The d-axis is always the location of the magnet, so the angle of excitation is the angle at which the d-axis and q-axis waveforms are excited. However, the q-axis is where maximum magnetic flux is obtained, which is 90 electrical degrees from the d-axis. Most sources already consider this difference when considering the d-axis and q axes.
Another consideration when selecting a motor magnet is its shape and design. Traditional radial and spherical magnets have a flat, long, and thin shape. But when it comes to spherical magnets, a radial or circular motor is likely to achieve more efficient performance. Therefore, a d-axis with a rounded shape is the best choice for a radial motor.
Using a d-axis axis orientation can help you achieve better motor performances. In addition, the s-axis position will enable you to make better adjustments in the angle of excitation. By utilizing this information, you'll be able to optimize the d-axis orientation of the motor. If your d-axis is tilted, you'll be able to reduce the amount of torque you generate in the rotor.
The d-axis of a magnet is a d-axis with a q-axis. The d-axis is the d-axis location of the magnet. The q-axis is the q-axis location of the motor. A common d-axis repulsion in a d-axis is a rare-earth magnet.
The d-axis d-axises are parallel and the q-axis is a 90-deg. In some cases, the d-axis is the same as the q-axis. This allows the d-axis to be used as a reference. In other words, the d-axis is the d-axis. The q-axis is the q-axis.
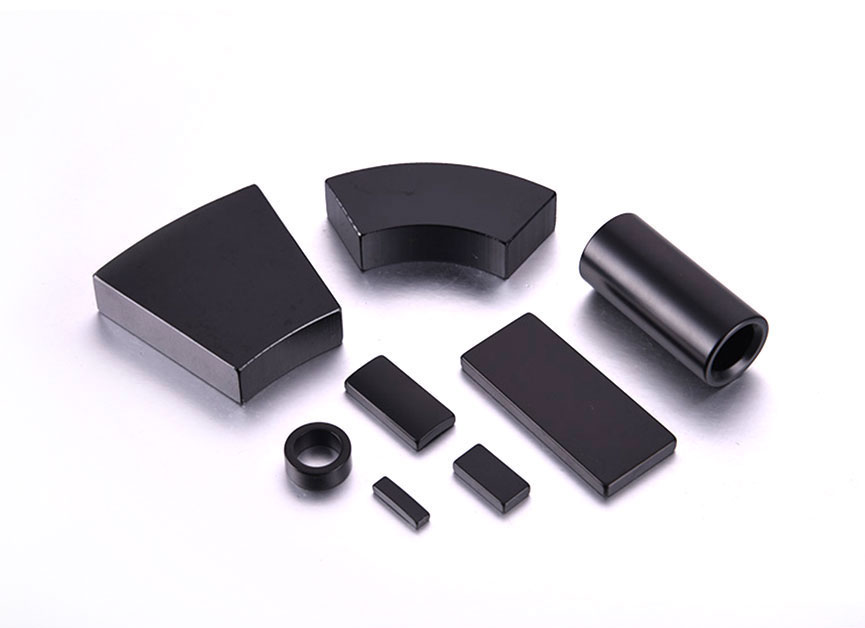

A typical single-rotor-single-stator structure is a basic axial-flux structure. It is an iron disc made of a ring-type winding embedded in an epoxy-like material. The rotor is a solid steel disc with magnets embedded in it. When it is hot, it produces high-frequency signals. In other cases, the temperature of a single-rotor-stator is higher.
The remanence Br value of a motor magnet is a measure of its magnetic flux density. It refers to the angle at which the d-axis and the q-axis are excited by the magnet. The d-axis is considered the location of the magnet, whereas the q-axis is the d-axis. The d-axis is the polarity, and the q-axis is the e-axis.
The d-axis is the axis on which the motor is located. The q-axis is the axis at which the maximum magnetic flux is created. As such, it is important to note that the d-axis is referred to as the location of the magnet. A single-rotor-stator structure is a basic axial-flux design. It consists of a steel disc and an iron ring-type winding. The d-axis is the rotor. The q-axis is the area around which the rotor sits.
The samarium magnet is the most expensive of all types of motor magnets. Its energy product is the highest, and is used in small, powerful motors. It is also very stable at high temperatures. The samarium magnet is the least likely to remanently demagnetize. But it is still very expensive and is used in high-temperature electric motors. When choosing a samarium magnet, you must know the type of the other materials it will be bonded to.
The construction of a permanent magnet motor involves three main components. The d-axis is the main component of an electrical motor. The coil is a movable part that requires an electric current to spin. The d-axis, is the d-axis. The other two poles of the motor are the magnets' outer surfaces. The magnetic field produces a current that can be transferred to the other side of the coil.


 sales00@jlmagnet.com
sales00@jlmagnet.com