What is the working temperature of sintered NdFeB? In fact, the maximum working temperature of most magnetic materials is much lower than its Curie temperature. The magnetic force will decrease when the temperature rises within the working temperature of sintered NdFeB, but when the temperature does not exceed the Curie temperature, most of the magnetic force will be lowered after cooling. Will recover.
Definition of temperature coefficient of remanence of sintered NdFeB
The temperature coefficient of remanence of sintered NdFeB, as the name implies, is the relative change rate of physical quantity with temperature. From the reference temperature T0 to a certain high temperature T, the temperature coefficient of remanence of sintered NdFeB is defined as follows, the unit is %/℃.
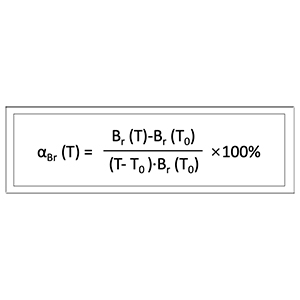
Among them, Br(T) and Br(T0) are the remanence at the temperature T and the reference temperature T0 respectively. Usually room temperature or 20°C is selected as T0, and the value of high temperature T needs to be determined by both the supplier and the demander according to the use environment. If αBr is positive, it means that the remanence increases as the temperature increases; if it is negative, it means that the remanence decreases as the temperature increases.
The relationship between the working temperature of sintered NdFeB and the Curie temperature: the higher the Curie temperature, the higher the working temperature of the material, and the better the temperature stability. The addition of cobalt, terbium, dysprosium and other elements to the sintered NdFeB raw material can increase its Curie temperature. Therefore, high coercivity products (H, SH,...) generally contain dysprosium.
What is the degree of sintered NdFeB? The Curie temperature represents the theoretical working temperature limit of magnetic materials. The Curie temperature of NdFeB is 320-380 degrees Celsius. The level of the Curie point is related to the crystal structure formed by the sintering of the magnet. What is the degree of sintered NdFeB? N low coercivity: 80℃, M medium coercivity: 100℃, H high coercivity: 120℃, SH super high coercivity: 150℃ UH super high coercivity: 180℃.
What is the Curie temperature of a neodymium iron boron magnet? Neodymium iron boron, also known as neodymium iron boron magnet (NdFeB magnet), is a tetragonal crystal composed of neodymium, iron, and boron (Nd2Fe14B). Founded in 1982 by Masato Sagawa of Sumitomo Special Metals, Japan, it is the strongest permanent magnet today.
What is the Curie temperature of a neodymium iron boron magnet? The Curie temperature of NdFeB is 320°C-460°C. The applicable ambient temperature of ordinary neodymium iron boron magnets is below 80 degrees, but there are also several types that can withstand high temperatures of 200 degrees.
NdFeB permanent magnet materials have excellent magnetic properties, extremely high magnetic energy product and coercivity, and high energy density. They are widely used in electronics, electrical machinery, medical equipment, toys, packaging, hardware machinery, aerospace, etc. In the field, the more common ones are permanent magnet motors, speakers, magnetic separators, computer disk drives, magnetic resonance imaging equipment and meters, etc.


 sales00@jlmagnet.com
sales00@jlmagnet.com